Topological Sort
A topological ordering is an ordering of the nodes in a directed graph where for each directed edge from node A to node B, node A appears before node B in the ordering.
For example:
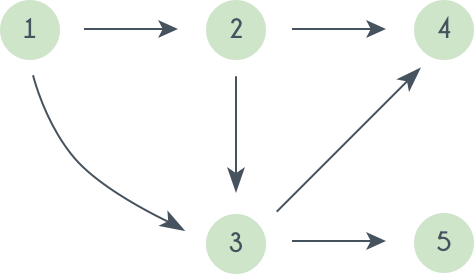
A topological sorting of this graph is: 1 2 3 4 5
Topological ordering are NOT unique. For the graph given above one another topological sorting is: 1 2 3 4 5
Note: Not every graph can have a topological ordering. A graph which contains a cycle can not have a valid ordering.
1. Kahn's algorithm
Algorithm Steps:
- Compute in-degree (number of incoming edges) for each of the vertex present in the DAG and initialize the count of visited nodes as 0.
- Pick all the vertices with in-degree as 0 and add them into a queue (Enqueue operation)
- Remove a vertex from the queue (Dequeue operation) and then.
- Push node to topological array.
- Decrease in-degree by 1 for all its neighbouring nodes.
- If in-degree of a neighbouring nodes is reduced to zero, then add it to the queue.
- Repeat Step 3 until the queue is empty.
- If size of topological array is not equal to the number of nodes in the graph then the topological sort is not possible for the given graph.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | |
2. DFS
Algorithm Steps:
- Pick an unvisited node
- Begin with the selected node, do a DFS exploring only unvisited nodes
- On the recursive callback of the DFS, add the current node to the topological ordering in the reverse order
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | |